The DNA genetic material of cells changes configuration when undergoing reproduction and repair. As a result, the chromatin* fibers of DNA become more open to chemical changes. These changes occur due to methylation (addition of a methyl group) of the DNA and acetylation (change of an acetyl group). The amount of acetylation is due to a balance of enzymes called histone acetyl-tranferase and histone deacetylases (HDACs). The later make the chromatin DNA fibers more condensed and more difficult to alter.
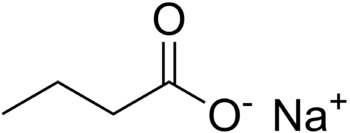
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) alter tumor growth and spread, reduce proliferation and migration, while increasing apoptosis (natural cell death) and differentiation of cancer cells. Many tumors have abnormal HDAC behavior so that HDACIs are widely used in anticancer treatments. Some have been approved by the FDA for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Sodium butyrate is an active HDACI in the millimolar range. HDACIs have milder effects on normal cells compared to cancer cells.
HDACIs have uses other than for cancer treatment. Studies have been done for use in HIV, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), malaria, neurodegenerative disease, cardiac hypertrophy and asthma.
Abnormal acetylation may be the cause of neurodegenerative diseases. Trichostatin A, butyrates and valproic acid have been studied, and Trichostatin A, an HDACI, can restore long-term memory loss. In general, HDACIs restore histone acetylation, increase the growth of nerve cells, and reduce neuroinflammation.
Improved acetylation reduces inflammation and, as well, dopaminergic cell death in Parkinson’s disease. It, also, benefits Huntington’s disease. Valproic acid, sodium butyrate, phenylbutyrate, and Trichostatin A have shown some benefit in models of Alzheimer’s disease. HDACIs have shown benefit in cardiac hypertrophy, however not all treatments have been beneficial and more research is needed.
HDACIs are being studied in asthma. So far, the effects are controversial. Trichostatin A improved airway hyperresponsiveness, but not inflammation in asthma in animals. However, resveratrol, a class III HDAC agonist, inhibited inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of allergic airways disease.
CONCLUSION: HDAC inhibitor usefulness extends beyond cancer treatments. Investigation continues in neurodegenerative diseases, cardiac hypertrophy and asthma.
NOTE: Alternative products which alter histone acetylation include resveratrol, sodium butyrate, curcumin, retinoic acid (a form of vitamin A), chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, and phenylbutyrate.
*Chromatin is a combination of DNA and protein which makes up the nucleus of a cell.
To read the author’s abstract of the article, click on the title of the article. Then, to read the full article, click on the full text icon.
PMID: 22046487.
Summary #651.